Anthropology of Art
Overview
Course Code
SAB60101
Credits
2
Semester
I
Frequency
Odd
Type
General Course
Class Size
55
Duration
16 meetings
Student Workload
119 hours
Contact Hours
35 hours
Independent Study
42 hours
Description
This Anthropology of Art course will discuss art and cultural expressions that are always related to people's daily lives. The course will examine artworks such as paintings, murals, sculptures, crafts, performances, films, and music reflected in cultural, social, historical, and political contexts. The course will provide an in-depth understanding of art and its role in shaping the human world while providing insight into the diversity of cultures.
Course Content
- What is art? What is Aesthetics? What is anthropology of art?
- The relevance of Anthropology in Art research
- Artistic data collection methods
- Images and culture
- Tradition art
- Mural
- Handicrafts
- Music
- Cinema
- Dance Art: Dancing on a mass grave.
- Anthropologist as artist
Reference
Primary Literature
- Lee, Doreen. 2013. “Anybody Can Do It”: Aesthetic Empowerment, Urban Citizenship, and the Naturalization of Indonesian Graffiti and Street Art.” City & Society 25 (3): 304-327.
- Nakashima Degarrod, Lyda. 2020. “The Anthropologist as Artist.” Website, November 16.2020
- Sansi, Roger. (2022) 2023. “Art”. In The Open Encyclopedia of Anthropology, edited by Felix Stein. Facsimile of the first edition in The Cambridge Encyclopedia of Anthropology. Online: http://doi.org/10.29164/22art
- Sharman, Russell. 1997. “The Anthropology of Aesthetics: A Cross-Cultural Approach.” Journal of the Anthropological Society of Oxford 28, no. 2: 177–92.
- Simatupang, G.R. Lono Lastoro. (2013) Pergelaran: Sebuah Mozaik Penelitian Seni-Budaya. Yogyakarta: Jalasutra
- Simatupang, G.R. Lono Lastoro (2002). Play and Display: An Ethnographic Study of Reyog Ponorogo, East Java, Indonesia. Ph.D Dissertation, Sydney: University of Sydney.
- Taussig, Michael. 2011. I Swear I Saw This. Chicago: University of Chicago Press.
Supporting Literature
- Ahimsa-Putra, Heddy Shri. (2000). Ketika Orang Jawa Nyeni. Yogyakarta: Galang Press.
Assessment System
Assessment Matrix
- Participatory Activity 20%
- Assignment 20%
- Midterm Exam 30%
- Final Exam 30%
Peer-Assessment
The percentage of student contribution is taken from the score given by group members to other group members (peer-assessment) regarding the contribution in the process of working on the task from beginning to end.
- Score 100% if the assessed member fully participates from start to finish
- Score 75% if the assessed member participates actively, although sometimes less involved
- Score 50% if the assessed member participates, although often not involved
- Score 25% if the assessed member only appears at the beginning/middle/end only
- Score 0% if the assessed member is not involved at all
- The student contribution percentage score is the total number of peer-assessments divided by the number of group members who were assessed
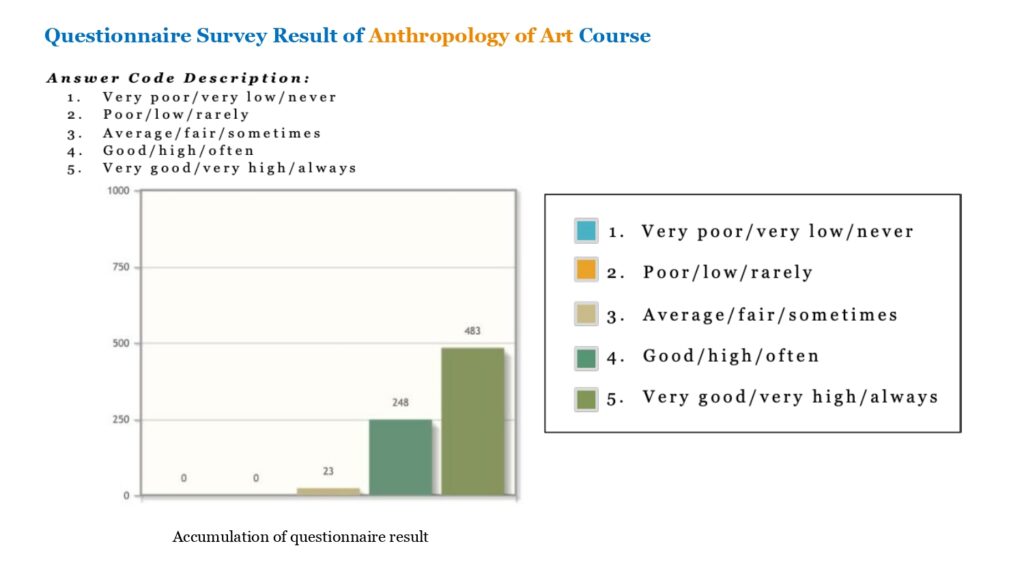
Students Feedback